The Decentralized Biomedical Solution on the Octopus Network
The current biomedical system is broken. The status quo prevents patients from being able to access their data freely, and healthcare providers can’t guarantee the safety of their patient’s data. The DeBio Network aims to change that.
What is DeBio Network?
DeBio Network is a decentralized anonymous-first platform for medical and bioinformatics specializing in genomic testing. DeBio aims to revolutionize the current biomedical industry by giving patients full sovereignty over their data using the most cutting-edge blockchain technologies.
The introduction of blockchain in the current tech ecosystem plays a big role in the pursuit of decentralized global finance, but the use cases offered by blockchain exceed more than just finance. DeBio believes that the future of medical data relies partly on the use of blockchain, especially in the specialization of technology use cases as well as interoperability.
Centralized Genetic Testing Is A Privacy Risk
For the past few years, genetic testing has exploded in popularity. As a result, direct-to-consumer genetic testing platforms such as 23andMe, and AncestryDNA have seen an increase in consumers. But what many people fail to realize is the implicit privacy risk of using these platforms.
Mainstream direct-to-consumer genetic testing platforms are centralized, making them an easy target for data breaches. In 2020, there were 1001 data breaches in the United States alone; with the healthcare industry receiving the brunt of it, Govtech reported.
Even more concerning is that genetic data is not unique to an individual but unique to the individual’s family tree. By using a centralized bioinformatics service you put at risk not only your privacy but also the privacy of your distant relatives.
The harm of this is unambiguous because there is a possibility that your distant relatives, for example, a second cousin can be affected by your decision. Worrisome is the thought of a distant relative you don’t even know exists, taking a genetics test and having their genetic data be traced back to you.
Genetic data can be traced back to you even with a little amount of demographics information, such as their age and state. This type of information can be used against you by insurance companies, to make the most of their clients.
The DeBio Network Concept
The main concept behind DeBio is based on the notion of wanting to increase biomedical and genetic testing to consumers without forfeiting their privacy. But DeBio also wants to incentivize genetics research by offering collaborations between sovereign labs.
A Physical-To-Digital Bridge for Anonymous Testing
Consumers can select a wide range of products and laboratory recommendations from DeBio’s genetic testing marketplace. After the consumer has decided on a product they will only need to take two DNA samples via the buccal swab method or take samples of oral cells with cotton swabs.
The consumer then sends the DNA sample to the laboratory within an envelope with the only identifiable information written on the envelope is the genetic tracking ID for the sample. Laboratories cannot identify samples without a tracking ID because, for anonymity purposes, DeBio will not collect personally identifiable information of any kind, making the DNA samples untraceable back to the consumer.
The results (e.g, test and genome) are then encrypted with the consumer’s public key retrieved from the DeBio blockchain and stored then uploaded on decentralized storage. This allows consumers to maintain full sovereignty over their encrypted data — consumers must possess their private keys to decrypt the results.
The DeBio Network team is expanding this “physical-to-digital bridge” concept to use cases outside of the genetic testing market — which may include lab testing for diseases and other electronic medical record data or personal health information.
Sovereign Lab Collaboration To Offer Joint Products Integrating Services From Several Labs
After the consumer sends the DNA sample to the lab, the lab will be notified. When the sample arrives, the lab will begin sequencing the physical samples or will begin any biomarker tests. After finishing the subsequent tests, the lab will then encrypt the results using the consumer’s public key and upload them to decentralized storage.
The results cannot be decrypted without the use of the consumer’s private key, thus the consumer’s sovereignty over their biomedical testing results is secure. However, to further incentivize genetic testing, consumers are opted to stake their genetic testing data to be used by other labs.
The goal of having sovereign labs is to increase the availability of products and enable joint products by integrating services from several labs. This also allows DeBio to scale because labs do not need to be centralized allowing for multiple standalone genetics facilities to participate.
Quiz: What problem does the DeBio Network intend to solve?
The DeBio Network Techstack
Bioinformatics and biomedical ecosystems both have unique demands in how they both need to be accessible to the professionals conducting the studies but also be secure enough to safeguard the patient’s privacy and sovereignty. Thus, to guarantee patient sovereignty over their data, the entire tech stack consists of decentralized solutions ranging from decentralized authentication to decentralized file storage.

Image is taken from DeBio Deck
DeBio has incorporated a slew of cutting-edge technologies in the solution, including but not limited to:
Substrate
The first notable tech incorporated is Substrate. Substrate is the framework behind the Polkadot token, enabling developers to build purposeful blockchains. The core services will be built using Substrate, making them the core building blocks of the solution. DeBio chose Substrate because of the two following reasons:
- Blockchain interoperability (essentially being able to communicate between different blockchains).
- Relay chain security (applying stricter security standards of the host relay chain).
Other than allowing blockchains to communicate with each other, the interoperability feature also enforces a security standard that will be inherited by each para chain connected to the main relay chain. As a result, the security of the DeBio blockchain is improved by following the standards of the corresponding relay chain.
KILT Protocol
The next notable mention would be the KILT Protocol. KILT is a protocol for creating, attesting and verifying identities anonymously on Web3. To authenticate themselves, each user needs to create a claim, that would then be sent to a trusted attester.
An attester has the responsibility of certifying a user’s claim, which will then transform into a hash to be saved on the KILT blockchain. A user’s claim sometimes contains sensitive data concerning the user, but because the hash cannot be transformed back into a user claim the user’s privacy is guaranteed.
After receiving the certificate from the trusted attester, the user can now use his/her claims on applications that use KILT and trusts the aforementioned attester. KILT is privacy by design. Applications that will verify the claim do not need to go through the attester and will directly compare the claim to the one stored in the KILT blockchain, cutting the attester off from the verification process and making it fully decentralized.
The KILT Protocol provides a solution that prevents data from being concentrated in one entity. It enables data sovereignty for the privacy-conscious. DeBio has partnered with KILT to implement a decentralized authentication system because it fits perfectly with DeBio’s anonymous-first use case.
The Octopus Network
Octopus is a crypto network for launching and running Web3 application-specific blockchains at the fraction of the cost. One of the considerations of using Octopus is that, compared to Polkadot, they offer a significantly cheaper security lease and comparable cross-chain capabilities. Octopus is backed by the NEAR Protocol, NEAR is a high-performance blockchain meant to solve the problem of scalability, and to increase developer productivity by simplifying the development process and creating a developer-friendly environment.
DeBio is already partnered with Octopus and will be one of the first five application-specific blockchains (app chains) launched on the Octopus Network. DeBio is also already part of the Octopus Guild, a community of developers and app chains on the Octopus Network.
The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS)
The InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) is a protocol made for fully decentralized, peer-to-peer data sharing and storage. IPFS was created as a solution for decentralized projects that want to store an amount of data that is too large to be stored in the blockchain itself. IPFS creates unique content addresses by hashing the content itself. Each unique content will have a different address pointing to its location. DeBio adds IPFS to store biomedical data such as encrypted human genomes and encrypted electronic medical records.
Ocean Protocol
The Ocean Protocol is built for the consumption of data assets in a secure, privacy-preserving fashion. It does this with the compute-to-data feature and enables the monetization of data without ever having to leave the owner’s premises. The Ocean Protocol’s open-source data marketplace called the Ocean Market is forkable; the DeBio Network team will use Ocean for biomedical data staking.
Privacy Computing
To stake biomedical data, DeBio will host anonymous biomedical data in their private data store. This process doesn’t involve the aforementioned IPFS because the data store will be completely separate from IPFS. Users who want to stake their data will need to decrypt and upload their biomedical data to their privately-held data store. While transferring decrypted biomedical data to a privately-held data store sounds eerie, DeBio will implement privacy computing concepts within the data store to safeguard your privacy.

Image retrieved from DeBio Whitepaper
Only after the user’s consent are the datasets aggregated through Ocean’s compute-to-data proxy, and the 3rd party will be able to create analytics and process the data all the while it remains on-premises.
By incentivizing users to stake their genomic/biomedical data, and hope that it would further incentivize research in the field. Moreover, the privately-held data store will not be gathering personally identifiable information thus there is no need to worry about your samples being traced back to you.
Pandu Sastrowardoyo, the CEO of DeBio, stated that one of the reasons she created DeBio is to help genetic research flourish by creating a fully anonymous genetic data marketplace. “DeBio is a whole new economic system for genomics — allowing genetic sovereignty, ensuring participation of smaller labs while supercharging genetic research. All done on top of a DeFi-like model that is fully decentralized,” said Pandu.
Quiz: Where does DeBio store the staked data?
Technical Architecture Layers
Our technical architecture consists of four layers, the main blockchain infrastructure, the transport and generic business logic layer, and lastly the top-level business logic layer.
DeBio Proposed Technical Architecture, Image retrieved from DeBio Whitepaper
Layer 1: The Blockchain Infrastructure
The first layer will contain the core services. The core services are built on top of Substrate, Octopus, and IPFS. Substrate is the core building block for the blockchain service. To save large files DeBio will use IPFS and save the content address inside Substrate instead. Finally, the entire app chain will be connected with the Octopus relay chain.
Layer 2 & 3: The Transport and Generic Business Logic Layer
The second and third layers contain the transport and generic business logic. These layers are responsible for serving data directly to the users. Each pallet contains the base business logic for interactions with the blockchain and will serve as an abstraction layer from the fourth layer to communicate with Substrate services on the first layer.
Layer 4: The Top-Level Business Logic Layer
The fourth layer would consist of the DeBio UI and Metamask. All interaction between the users and the blockchain will be done from the fourth layer. All queries will also be defined from the top level, and will then be processed on all the previously mentioned layers. To fund each transaction, users can use Metamask to pay using an ERC20 stable coin. In this case, DeBio will be using DAI as the stable coin of choice.
The Token Model
Image retrieved from DeBio Whitepaper
The DeBio Network team intends to release six tokens:
- Mainnet Transaction Rewards & Validator Token ($DBIO)
- The Governance Token ($GBIO)
- The Genomics Data Token ($GENE, via Ocean Protocol)
- The Biomed Data Token ($MED, via Ocean Protocol)
- The Electronic Medical Records Data Token ($EMR, via Ocean Protocol)
Mainnet Coin (stable coin, etc)
The mainnet coin will be backed by a stable coin. DeBio decided to use a stable coin because it needs to be used as a stable exchange for transactions, and fees related to the work being done by the corresponding labs. DeBio is going to utilize $DAI as our stable token.
Governance Token ($GBIO)
Governance tokens will be used mainly for voting by the registered labs. DeBio Network is a decentralized organization so there needs to be a governance scheme in place for voting in the DAOGenics marketplace. Alternatively, the governance token can also serve as a method for lab onboarding.
The Data Tokens ($GENE, $MED, and $EMR)
These tokens are used as a method of transaction in the data marketplace. When staking biomedical data on the Ocean marketplace the consumers will be rewarded with data tokens that can be converted to $OCEAN.
Validator & Transaction Rewards ($DBIO)
The validator token is used to incentivize the node owners to validate transactions and secure the dApp from unauthorized users. The intended incentives provided for validators are LP rewards and governance tokens.
Consumer Transactions In DeBio Network
$DAI is the mainnet stable coin used for transactions on the DeBio platform. Consumers can use the mainnet coin to pay for products and service fees. Products that will be available in the marketplace include genomic testing products, biomedical testing products, and a sovereign electronic medical records storage service (EMR).
Image retrieved from DeBio Whitepaper
Transactional Rewards
Each transaction committed by the consumer will be rewarded by a validator token, more specifically a $DBIO token. The price of a single $DBIO token is determined by the DeBio Network data marketplace that houses the consumer genomic data available for staking.
Data Staking In DeBio Network
After buying a product on the marketplace, the consumers can opt to stake their results on the Ocean Marketplace. Data Staked by consumers will be categorized as data tokens, called $GENE, $MED, and $EMR for genomic data, biomedical data, and electronic medical records (EMR) respectively. The data tokens will be kept in the DeBio Network and aggregated to the data marketplace via Ocean Protocol as an ERC20 token. Because the genomic data, biomedical data, or EMR itself is too large to be saved inside the ERC20 data tokens, the data tokens will primarily serve as a pointer/link to the corresponding data.
Consumers who stake their data tokens will have a “data provider” role in the data marketplace. All transactions in the Ocean data marketplace will use $OCEAN tokens. Thus, if the transaction is successful, the buyer will be exchanging $OCEAN tokens for the data tokens ($GENE or $EMR or $MED). Whereas the “data provider” will receive the subsequent $OCEAN tokens.
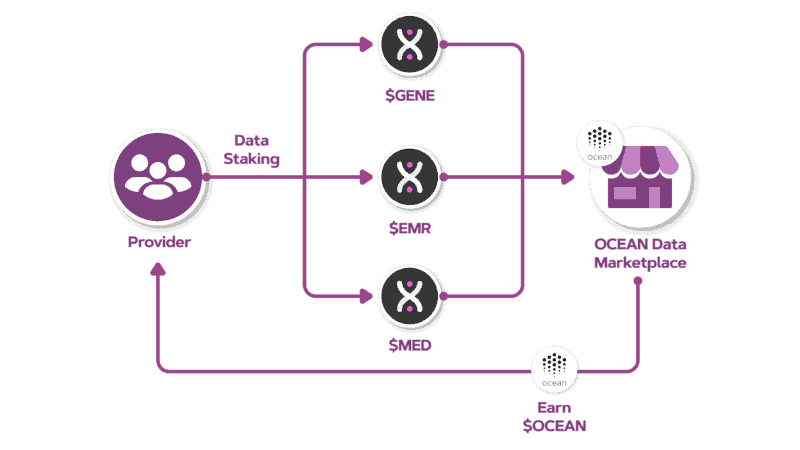
Image retrieved from DeBio Whitepaper
If the data buyer wants to access the data linked in the data token, they need to send the data token to the data provider beforehand. As a result, the data provider will have both the $OCEAN token and data tokens while the data buyer will be sent the data linked by the data token.
Image retrieved from DeBio Whitepaper
Conversely, data tokens ($GENE or $MED or $EMR) received by the DAOGenics Foundation will be converted into $OCEAN tokens. After a certain period, the $OCEAN token received by DAOGenics Foundation will be converted into a $DBIO token through a non-permission smart contract.
As a result, DAOGenics Foundation will always buy back the $DBIO token through a non-permission smart contract based on transaction volume conducted in the data marketplace. More transactions in the data marketplace will increase demand for the $DBIO token.
Quiz: When you stake data on the DeBio Network data marketplace, what do you earn?
Conclusion
There are many benefits of doing genetic testing. For the first time in the history of humanity, people have been able to determine their lifestyles to pursue longevity; the advantage of such knowledge is astounding. But while genetic testing has its wonderful benefits without proper regulations and standards it also has its shortcomings. Without the guarantee of having your genetic data private and secure, it could cause problems in the future.
DeBio aims to solve the problem before it’s too late. DeBio is building a decentralized platform for your personal medical needs, starting with genetics. Our concept allows synergy between labs of all scales while guaranteeing user anonymity and sovereignty at every step of the genomic data science workflow — from sample collection, data storage, to report generation.
Some people might say that our DNA is the most private thing we have, and we take that very seriously. Anonymity-first genetic testing should be the number one focus for all companies.
The future is here, DeBio is creating solutions to revolutionize the healthcare and genetic testing industry. Are you ready to change the world with us?
Adapted from the original article on Medium.
Updated: October 4, 2021




great article)