You’ve probably come across the expressions “if it’s free, you’re the product” or “data is the new oil,” and laughed it off as a silly little saying. The truth is data is the driving force behind nearly all businesses and services. For example, personalized experiences and services, marketing, and a host of other insights and services depend on the volume and quality of data provided to them. Most companies are eager to access data to help understand their customers better, predict customer behavior patterns, and improve the quality of their services.
The traditional space has always been subject to concerns surrounding data and privacy. Privacy advocates have long flagged concerns about how data is stored, how it is accessed, and who has access to it. With the growth of the cryptocurrency and blockchain ecosystem, similar concerns have also arisen in this sector. The public nature of blockchains has introduced several privacy concerns for users regarding safeguarding their personal information. This article will take a closer look at the privacy problem on blockchains and how Zero Knowledge (ZK) proofs can mitigate them.
What Is Data Privacy?
The increase in internet usage has brought the issue of data privacy into the mainstream, with nearly all websites, applications, and social media platforms collecting and storing users’ personal information to provide certain services. However, these platforms and websites often do not have adequate safeguards in place to secure the data collected, resulting in numerous data breaches.
With the growth of blockchain technology and the crypto ecosystem, there have been growing concerns about the privacy of retail and institutional users. These concerns are primarily due to the public nature of blockchains, with most Layer 1 and Layer 2 solutions failing to address these issues. Data privacy refers to the ability of users to determine, at their end, when and how their information is shared with others. It also encompasses the ability of users to dictate to what extent their data is shared. This information can include their names, location, contact information, online behavior, likes, dislikes, transaction details, and more.
Trust, Privacy, And The Blockchain
At present, the cryptocurrency ecosystem is undergoing considerable upheaval following the collapse of major projects such as FTX. However, the underlying technology supporting cryptocurrencies has the potential to revolutionize privacy, trust, and how trust is leveraged. This is critical in the internet age when millions browse and share copious amounts of their personal information to access services and products.
Blockchain technology inherently comes with problems around privacy, thanks to its design. The decentralized nature of blockchains means that nodes processing the transactions or information have access to the blockchain data. For example, the Bitcoin blockchain is publicly available and can be accessed by anyone who wishes to check its transaction history right up to its genesis block. Now, remember, Bitcoin is pseudo-anonymous, which means “[d]ata points which are not directly associated with a specific individual [but where] multiple appearances of [a] person can be linked together.”
Enough pseudo-anonymous data makes it possible to identify individuals behind transactions, which is concerning for blockchain users, and there are several reasons for this. Unlike data that is used by regular applications, which is accessible only to a few, blockchain data can be scrutinized by everyone, which also includes malicious actors and entities that can exploit the information on the blockchain for their gain. Additionally, the immutable nature of the blockchain means that transactions and data will be permanently linked to the individual. This can be done by monitoring communication between nodes. Additionally, crypto wallets can also be analyzed without access to private keys, further complicating matters.
One high-profile example of using blockchain data to track an individual was the investigation and arrest of Ross Ulbricht, the individual behind the infamous “Silk Road” darknet website, which was used for various illegal activities. Law enforcement agencies identified Ulbricht as the individual behind Silk Road, thanks to blockchain data. Furthermore, they could track Bitcoin transactions and determine that a US Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) agent was laundering BTC connected to Silk Road. In this case, law enforcement agencies were able to track the data available on the blockchain to identify a notorious individual. But imagine if malicious entities could track your data with such ease thanks to the public nature of the blockchain. The results would be devastating.
Introducing Zero Knowledge Proofs
Zero Knowledge Proofs were first talked about by Silvio Micali, Shafi Goldwasser, and Charles Rackoff in a paper titled “The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof Systems,” and are considered a fascinating innovation of cryptography that can be utilized in several scenarios. In the case of the blockchain, it can help enable secure and anonymous transactions. Zero Knowledge Proof, also known as Zero Knowledge Protocol, allows one party (the prover) to prove to the opposite party (verifier) that they know a specific value or information (x) without disclosing any information apart from the fact that they know the value or information in question (x). The challenge when it comes to Zero Knowledge Proof is to justify the possession of the information without revealing it or any other additional information. A Zero Knowledge Proof must satisfy the following criteria.
- Completeness – Let’s assume the statement is true. An honest verifier, correctly and faithfully following the protocol, will be convinced by the information given by the prover who is correctly following protocol.
- Soundness – Soundness means there should be no way for the prover to falsify any information or falsely convince the verifier. Falsification must be impossible.
- Zero Knowledge – If the statement by the prover is true, the verifier learns nothing other than the fact that the information is true.
The first two are considered properties of more general interactive proof systems, with the addition of zero knowledge transforming the verification process into a zero-knowledge proof. Due to a small possibility (soundness error) that a malicious prover may convince the verifier of a false statement, zero-knowledge proofs are considered probabilistic proofs rather than deterministic proofs. However, the soundness error can be mitigated to a negligible value.
A Zero Knowledge Proof must satisfy what criteria?
How Does ZKP Work?
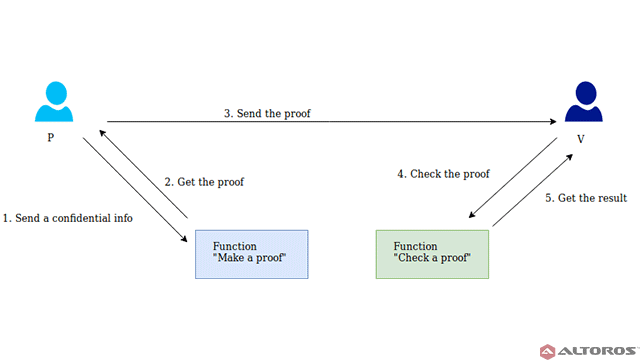
A Zero Knowledge Proof consists of three actions occurring sequentially between participants. These actions are called a witness, a challenge, and a response. Let’s delve a little deeper to understand the role of each action better by assuming there are two participants, A, and B.
Witness – Let’s assume A knows a specific value or information, which also determines a set of questions. These questions can always be answered correctly by A. Initially, A can choose any random question from the set, calculate the proof, and send it to B.
Challenge – After the witness step comes the challenge phase, where B chooses a question from the set and asks A to answer it.
Response – A then calculates the response and sends it back to B. This allows B to determine whether A actually knows the answer.
The process described above can be repeated as many times as required until it is established that A knows the correct answer and the probability of guesses becomes low enough.
The paper “The Knowledge Complexity of Interactive Proof Systems” was written by
Use Cases Of ZKP
ZKP can be applied in several scenarios.
Authentication Systems
Authentication systems have played a crucial role in fostering research in Zero Knowledge Proofs. In these systems, one party wishes to prove its identity to a second party through some secret information. However, it does not wish for the second party to gain any knowledge about this secret information.
Confidentiality
One of the most significant use cases of ZKP comes in transactions that require complete confidentiality. Let’s understand how. Consider a blockchain such as the Bitcoin blockchain. Generally, when a transaction occurs on this blockchain, data related to the transaction is recorded on the blockchain. This means anyone can piece together some amount of information about the transaction by analyzing the data on the blockchain. For the sake of privacy, it is critical to hide some details for specific transactions. ZKP makes it possible to hide details while also ensuring the transaction’s validity by adding them to a new block.
Personal Information
Say you wish to take a loan from a bank. To apply for the loan, you must furnish a host of documentation consisting of a considerable amount of personal information, making it available to third parties. In the case of obtaining a loan from a bank, the only information required by the bank is to know if an individual earns a specific amount enough to repay the loan. ZKP can help banks verify whether an individual earns a predefined minimum amount without revealing any sensitive information to the bank or any third party.
ZKP And Blockchain: The Way Forward
Several projects and cryptocurrencies utilize ZKP, such as ZCash, SmartCash, Zerocash, and ZeroVert. ZKP has mostly been implement via zk-SNARKS and zk-STARKS.. zk-SNARKS was originally developed by ZCash. Most blockchains are pseudo-anonymous, meaning a user’s identity could be traced back to their transactions by studying blockchain data. This information is available to everyone with access to the blockchain and could be exploited by any malicious entity.
Despite the blockchain’s reputation as the pinnacle of cybersecurity, this particular shortcoming is well-known to users. However, ZKP could help patch this vulnerability and ensure complete privacy when it comes to personal information. While ZKP still has quite a few challenges to overcome, it gives users control of their data and privacy, limiting access to third parties, and will play a crucial role in improving privacy when it comes to blockchains.



Top comment
the privacy implication in this seem magnificent. alternatively, i still think there should be a third party available for a short period of time directly connected to the blockchain involved. otherwise, whats stopping people from setting up faux loan recipients?
privacy is very important
There is a lot of useful information in this article
Это важная часть нашей жизни это изменит общество,конфидициальность это свобода.
As a human, I would say that providing personal information can be a concern when it comes to obtaining a loan from a bank. It's understandable to be hesitant to share sensitive information with third parties, especially when it comes to something as important as a loan. However, I would also say that it's important to be honest and transparent with the bank in order to ensure that the loan is approved and that the individual can repay it on time.In terms of the solution you mentioned, ZKP, I would say that it sounds like a promising technology that can help address some of the concerns around sharing personal information. It's great to hear that it can verify an individual's ability to repay the loan without revealing any sensitive information. This could potentially make the loan application process more secure and less invasive for the individual.
This article improved my knowledge so good about ZK data privacy, thankyou developer team!
Все классно
I believe that blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize many industries, but it is true that privacy concerns are a valid concern. The decentralized nature of blockchains means that there is no central authority controlling the data, which can make it more difficult to protect individual privacy. For example, the Bitcoin blockchain is publicly available and can be accessed by anyone who wishes to check its transaction history. This can make it easier for hackers or other malicious actors to access sensitive information. However, there are also ways to mitigate these privacy concerns. For example, some blockchain platforms use encryption to protect the data, or allow users to control their own privacy settings. Additionally, as the technology continues to evolve, I believe that we will see more solutions emerge to address these privacy concerns. Overall, I think that blockchain technology has the potential to be a powerful tool for many industries, but it is important to be aware of and address the potential privacy concerns that come with it.
It's interesting to consider the properties of more general interactive proof systems and how zero-knowledge proofs can transform the verification process into a zero-knowledge proof. While it's true that there is a small possibility of a soundness error, it's also important to note that this error can be mitigated to a negligible value. This means that while there is always some risk involved in using zero-knowledge proofs, it's still a viable option for many applications. It's important to carefully consider the specific use case and the potential risks and benefits before deciding to use zero-knowledge proofs.
As a human, I would say that while blockchain technology is known for its strong security features, there is always room for improvement. Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) are a promising solution to address one of the known vulnerabilities in blockchain, which is the lack of privacy when it comes to personal information. ZKP allows users to prove the validity of a statement without revealing any information about it, which can help protect sensitive data.However, I would also acknowledge that ZKP still has some challenges to overcome before it can be widely adopted. For example, it can be computationally expensive and may not be suitable for all types of blockchain applications. Additionally, there may be concerns around the security and reliability of ZKP protocols.Despite these challenges, I believe that ZKP has the potential to play a crucial role in improving privacy on blockchain. By giving users control over their data and limiting access to third parties, ZKP can help ensure that personal information is kept private and secure. As such, I would encourage further research and development in this area to help address the privacy concerns associated with blockchain technology.
Отлично
Hello. Thanks for information.